Overview of the Glow Worm Algorithm
Explanation of the original Glow Worm Algorithm
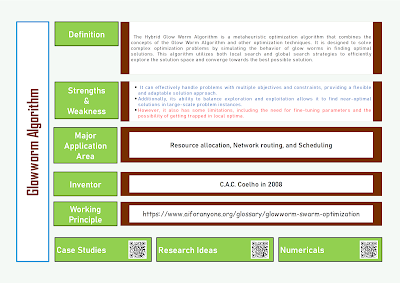
The Hybrid Glow Worm Algorithm is an important algorithm to study and understand because of its ability to effectively solve complex optimization problems. By combining the strengths of different algorithms, it offers a flexible and adaptable solution approach that can be applied to various domains. Understanding this algorithm can help researchers and practitioners in developing efficient and effective optimization strategies for their specific problem instances.
The original Glow Worm Algorithm is a swarm intelligence-based optimization algorithm inspired by the behavior of glow worms in nature. It involves a population of virtual glow worms that interact with each other and their environment to find optimal solutions.
The algorithm uses a combination of local and global search strategies, allowing the glow worms to explore and exploit the search space effectively. Additionally, the algorithm incorporates self-organization mechanisms, enabling the glow worms to dynamically adapt their behavior based on the problem at hand. This makes it a powerful tool for solving complex optimization problems in various fields such as engineering, logistics, and finance.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The Glow Worm Algorithm offers several advantages such as its ability to handle complex optimization problems, its adaptability to different domains, and its potential for finding global optima. However, it also has some limitations, including the need for fine-tuning parameters and the possibility of getting trapped in local optima. In terms of functioning, the Glow Worm Algorithm operates by simulating the behavior of glow worms in nature. Each virtual glow worm represents a potential solution and moves in search of better solutions based on a set.
One advantage of the algorithm is its ability to quickly converge to a near-optimal solution by leveraging both local and global search strategies. This makes it particularly suitable for problems with large search spaces. However, a limitation of the algorithm is that it may struggle to find the global optimum in highly complex and multi-modal optimization problems. Additionally, the algorithm's performance can be sensitive to its parameter settings, requiring careful tuning for optimal results.
For more detailed information about the Glowworm Optimization Algorithm, Case studies, Research Ideas, and Numericals visit the HydroGeek Post on GWO.