Data is the most important parameter of success in hydrological research. But measuring or collecting hydrologic data is complex due to its inaccessibility and financial requirements. For example, real-time stream level detection can help in the early warning of floods which can prevent/avoid “during” or post-flood disasters. Real-time dataloggers for stream-level detection are available but they are expensive. That is why low-cost alternatives like stream gauges are used.
However, the installation of such gauges in every location of a watershed is not possible as many places within a watershed are completely inaccessible. Again, the data collected by stream gauges are not real-time and not readily available to the researchers. One must pay or take permission from the regulating authorities to collect such data. Such requirements delay the project completion time and attract extra expenditures. Therefore, many ungauged or even gauged catchments remain unmonitored or sparsely monitored which in turn makes the flood or storm prediction models erroneous as most of them are data-driven.
That is why in recent years researchers are utilizing the data generated by the citizen scientist or crowdsourcing platforms which are easy to access and inexpensive. Sometimes technologies that are developed for some other objectives are also being used for monitoring hydrologic parameters due to their low cost and easy accessibility. This article tries to highlight seven such examples where low-cost, but easily accessible devices or crowdsourced data are utilized to monitor hydrologic parameters.
1. Sensors of windshield wipers used as mobile rain gauges
2. Parking Aid Sensors used to measure snow depth
3. Temperature Guns that are used to measure the temperature of a shipment were used for measuring the surface air temperature of the alpine valley
4. Soda bottles as rain gauges for ungauged catchments
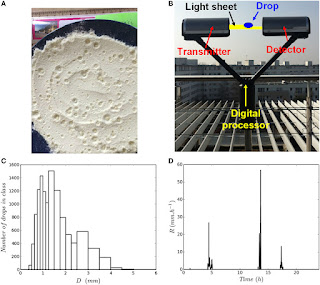
5. Sizes of Raindrops were determined by a homemade disdrometer, made of flour on a plate.
6. An app for measuring stream level without any physical installation of stream gauge but by using the citizen science concept of data collection
7. Volunteered Geographic Information(VGI)(User/Volunteer generated images of flood inundation) compared by using some technologies of Automatic Flood Detection
Thank you all for reading my blog.
This article is also available on Youtube/Slide Share
@data_hydrology ,
@Merchandise or @@products_sustainabilityAdd to Listy